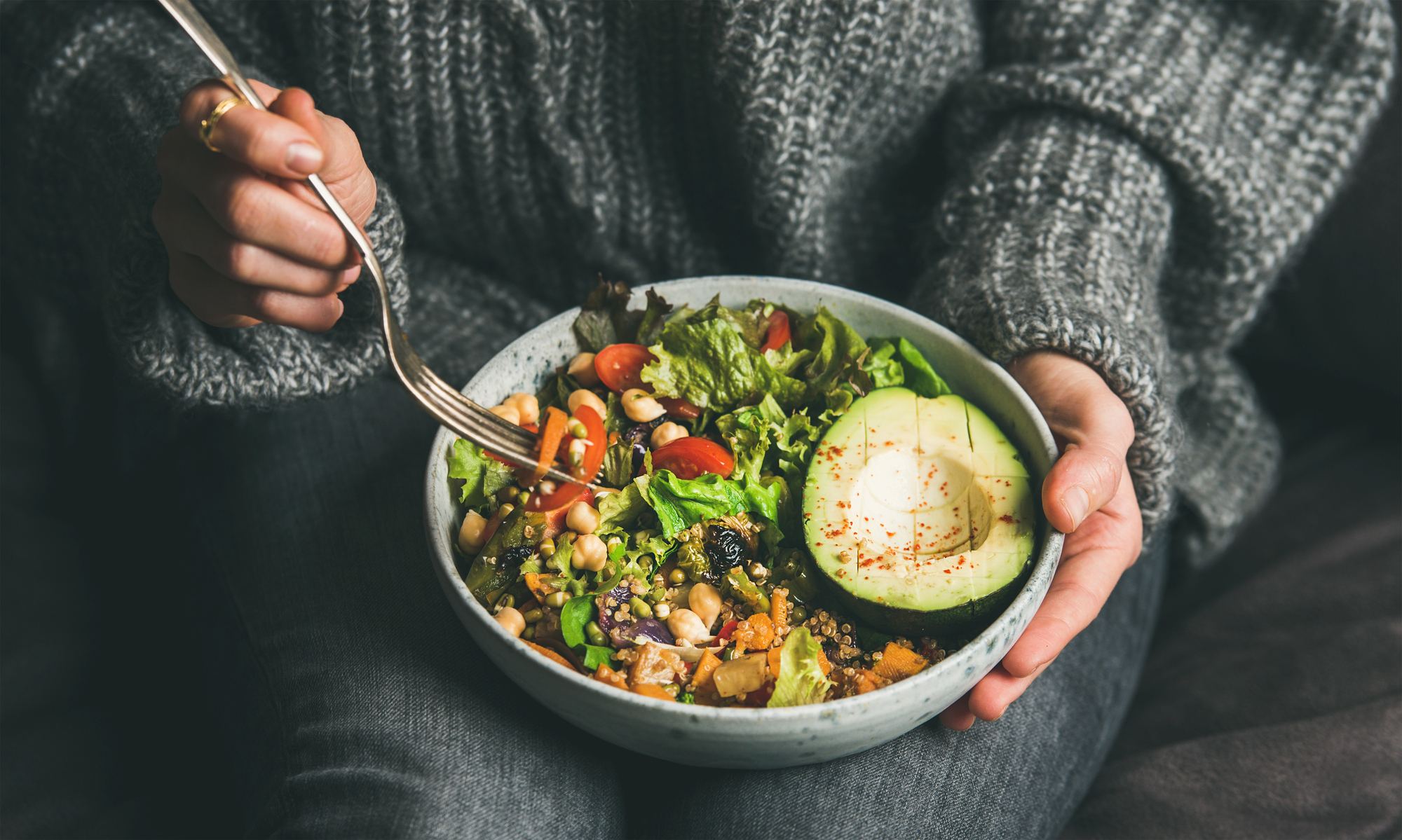
When you nourish your body with a plant-based diet, you are participating in a time-honored practice and are at the forefront of modern nutritional science. Plant-based nutrition offers a symphony of nutrients that can recalibrate your health. This is key to gut health and fighting inflammation in the body. A plant-rich diet prioritizes foods such as fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, and seeds, often limiting or eliminating animal product consumption. The nutrients in these whole foods are essential for maintaining a healthy gut, which is the foundation of overall wellness. Feeding your gut with high-fiber and nutrient-packed plant foods supports its healing processes and fosters a thriving microbiome.
The anti-inflammatory benefits of plant-based eating patterns are among their most compelling attributes. Chronic inflammation is a root cause of numerous health issues, and the antioxidants and phytonutrients found in plant foods can help reduce this inflammation. These natural compounds protect your cells and reduce the risk of inflammation-related diseases. Following a plant-based diet can also lead to improved energy levels. The efficient digestion of plant-based meals ensures a steadier release of energy, helping you avoid the peaks and troughs often associated with diets high in processed foods and sugars.
A commitment to eating plant-based nutrition is a commitment to your health. Research indicates that individuals who consume a diet high in plant foods and low in animal products have a reduced risk of developing chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. By choosing a plant-centered diet, you’re taking care of your present well-being and investing in your long-term health. This approach is not a quick fix or fad; it is a sustainable lifestyle that can enhance your physical and mental capacities, providing the clarity and vitality needed to enjoy life to the fullest.

Foundations of Plant-Based Diets
Plant-based diets center around foods originating from plants. These include various fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, and seeds. When you adopt a plant-based diet, your focus shifts towards whole foods, and you minimize or eliminate the consumption of animal products.
Incorporating these plant-based foods into your diet provides essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Each of these components plays a critical role in maintaining and improving your overall health. Here’s a simple breakdown of what to include in your plant-based diet:
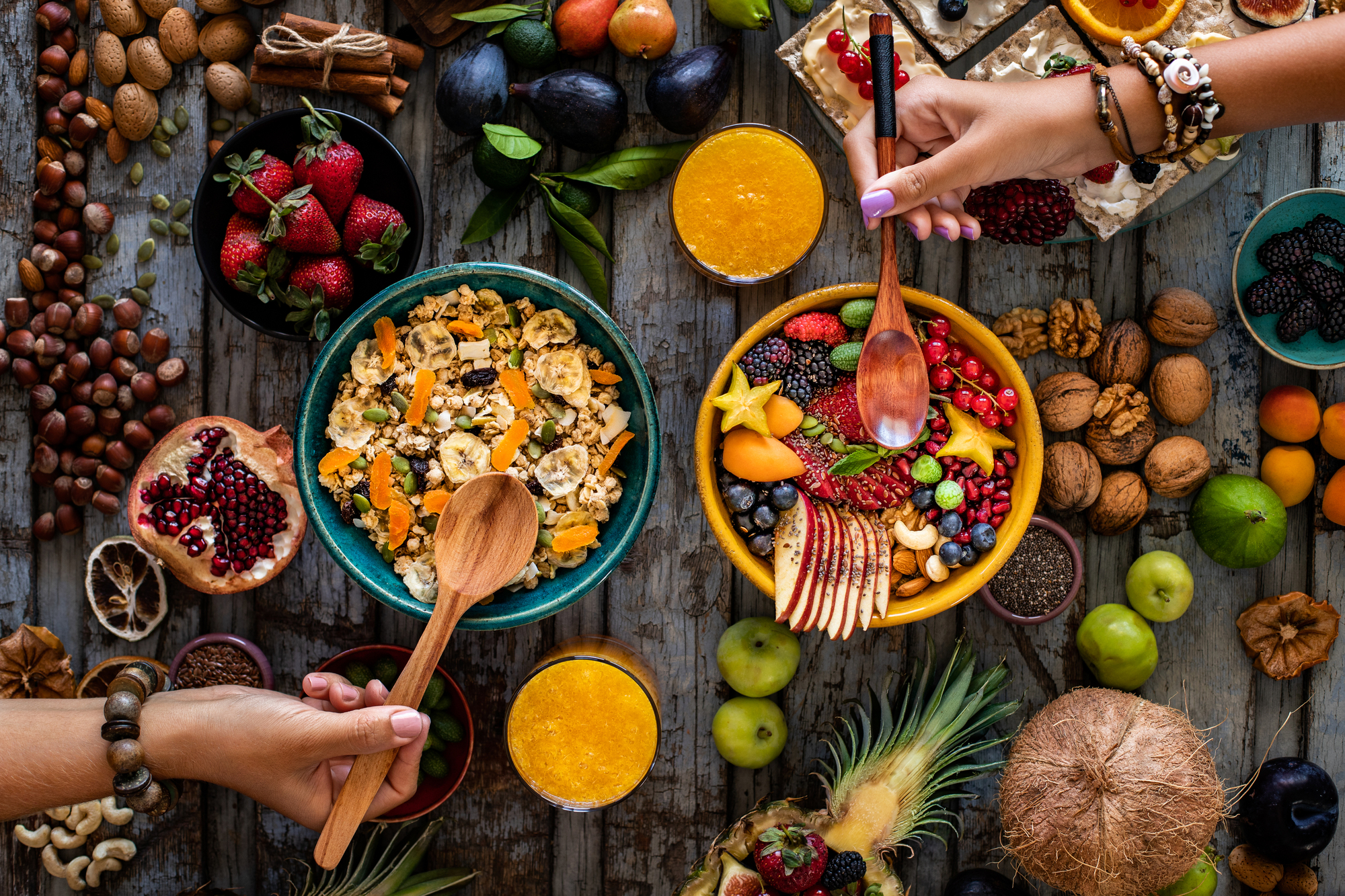
- Fruits and Vegetables: Aim for variety and color to maximize the range of nutrients. Eat the rainbow!
- Whole Grains: Choose brown rice, oats, and quinoa as staples for fiber and energy. Fiber is so important to implement in your daily diet.
- Nuts and Seeds: For healthy fats and protein, add almonds, chia seeds, and flaxseeds to your meals.
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, and beans are excellent protein sources and fiber-rich.
Your diet should prioritize unprocessed plants to ensure the most nutritional value. For example, choose fresh apples over apple juice or whole grains instead of refined bread. By doing so, you not only increase your nutrient intake but also help regulate your blood sugar levels and promote a healthy weight.
Remember to stay hydrated by drinking water throughout the day, which aids digestion and nutrient absorption. Transitioning to a plant-based diet can positively change your health, potentially alleviating certain chronic conditions and improving your energy levels. It’s essential to plan your meals to ensure you meet all your nutritional requirements.

Nutritional Benefits of Plant Foods
Plant-based foods packed with essential nutrients are vital for health. Incorporating various foods into your diet can support various body functions and promote overall well-being.
Vitamins and Minerals in Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are rich sources of vitamins and minerals crucial for your body’s functions. Here’s a snapshot of what they offer:
- Vitamin C: Found in abundance in citrus fruits, strawberries, and bell peppers, vitamin C is essential for immune function and skin health.
- Vitamin A: Crucial for vision and immune health, vitamin A is available in carrots, sweet potatoes, and kale.
- Potassium: Essential for heart function, muscle contractions, and maintaining healthy blood pressure, bananas, spinach, and potatoes are excellent sources of this mineral.
- Magnesium: Maintains normal nerve and muscle function and blood pressure and promotes calcium absorption. It is found in avocados, legumes, and leafy greens.
Proteins, Grains, Nuts, and Seeds
While animal products are known for their protein, plant-based nutrition also provides this essential macronutrient. Grains, nuts, and seeds deliver not just protein but a variety of other benefits.
- Quinoa and Amaranth: These gluten-free grains are complete proteins, containing all nine essential amino acids your body needs.
- Lentils and Beans: Besides protein, these provide fiber, which promotes gut health and improves digestion.
- Almonds and Walnuts: These nuts are protein-rich and contain healthy fats that support heart health.
- Chia Seeds and Flaxseeds: High in omega-3 fatty acids, these seeds can help reduce inflammation and boost brain function.
By choosing various plant foods, you ensure a diverse intake of proteins and other nutrients, supporting your health.

Gut Health and Plant-Based Eating
Adopting a plant-based diet can significantly improve gut health through microbiome enhancement and increased fiber intake.
Microbiome Enhancement
Your gut microbiome consists of trillions of bacteria, both beneficial and harmful. A plant-based diet can increase the diversity of your gut flora, which is crucial for your overall health. By eating a variety of plant-based foods, you introduce new types of bacteria to your system. These beneficial microbes thrive on the phytonutrients and fibers found in plants. An improved gut microbiome can help with nutrient absorption, boost your immune system, and even improve your mood.
Digestive Benefits of Fiber
One of the standout advantages of a plant-based nutrition diet is the high fiber content in fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes. Fiber is essential for:
- Maintaining regular bowel movements: A fiber-rich diet adds bulk to your stool, facilitating passage and alleviating constipation.
- Feeding your gut bacteria: Soluble fiber acts as a prebiotic, nourishing your gut bacteria. This leads to better digestion and reduced gut inflammation.
- Supporting detoxification: Fiber helps bind to toxins in the gut, allowing them to be flushed out of the body.
By concentrating on fiber-rich foods, you’re supporting digestive health and contributing to a more resilient, efficient gut.
Inflammatory Responses and Diet
Inflammation is a natural body process that can become chronic due to confident diet choices. Understanding the dietary influence on inflammation is crucial for managing and improving your health.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Plant Foods
Plant foods are rich in antioxidants and phytonutrients that fight inflammation in your body. Examples include:
- Berries: Contain anthocyanins, which reduce inflammation.
- Leafy Greens: High in vitamin K, essential for limiting inflammatory responses.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are packed with omega-3 fatty acids, which are known for their anti-inflammatory effects.
Incorporating a variety of plant-based nutrition into your diet can assist in reducing systemic inflammation.
Chronic Diseases and Inflammation Reduction
Chronic inflammation is linked to heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis. By choosing anti-inflammatory plant-based foods, you may reduce your risk. Consider these specifics:
- Whole Grains: Foods like quinoa and brown rice can lower C-reactive protein, a marker of inflammation.
- Legumes: Beans and lentils help manage blood sugar levels, which are critical for reducing inflammation.
- Herbs and Spices: Turmeric and ginger contain compounds that possess potent anti-inflammatory properties.
Selecting these foods may diminish the impact of chronic diseases by directly addressing inflammation.

Energy Optimization Through Plant Diets
Adopting a plant-based diet can significantly enhance your daily energy levels. You can achieve efficient and lasting energy throughout the day by choosing the right plant foods and balancing your meals.
Plant Foods for Sustained Energy
Consuming a variety of whole-plant foods is vital to maintaining steady energy levels. Here are specific choices that support sustained energy:
- Complex Carbohydrates: Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and oatmeal break down slowly, providing a steady release of energy.
- Fiber-Rich Foods: Legumes, such as lentils, beans, and chickpeas, are high in fiber, helping to regulate blood sugar levels.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, chia seeds, and flaxseeds contain healthy fats and proteins, contributing to longer-lasting energy.
Balanced Meals for Energy Efficiency
To optimize energy levels, your meals should have a strategic balance of nutrients:
- Proteins: Include plant-based proteins like tofu, tempeh, and edamame to aid muscle repair and sustained energy.
- Fats: Utilize healthy fats such as avocados and olive oil to help slow digestion, prolonging the feeling of fullness and energy availability.
- Variety: Incorporating a diverse array of vegetables ensures a spectrum of vitamins and minerals to support overall metabolism and energy production.
Mental Well-being and Nutritional Choices
Your dietary choices can impact your physical health and mental well-being. A plant-based diet, rich in essential nutrients, has been shown to support cognitive function and mood regulation.
Cognitive Benefits of Plant-Based Nutrition
Your brain requires a range of plant-based nutrition to function optimally, such as omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, which are plentiful in plant-based diets. Omega-3s are crucial for brain health in flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. Antioxidants combat oxidative stress, which can damage brain cells, and are abundant in berries and leafy greens. Furthermore, B vitamins from whole grains and dark leafy vegetables aid neurotransmitter function and energy production.
- Sources of Omega-3s:
- Flaxseeds
- Chia seeds
- Walnuts
- Antioxidant-Rich Foods:
- Berries (blueberries, strawberries)
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale)
- B Vitamins Providers:
- Whole grains (brown rice, quinoa)
- Dark leafy vegetables (broccoli, spinach)
Mood and Food: The Connection
The food you consume can directly affect your mood. Certain plants contain compounds that aid in producing serotonin, a neurotransmitter contributing to happiness and well-being. For example, bananas and oats are rich in tryptophan, which the body converts into serotonin. Complex carbohydrates from plants provide a steady supply of glucose, your brain’s primary fuel, stabilizing blood sugar levels and, thus, your mood. Additionally, the fiber in plant foods helps maintain gut health, which is also linked to mental health due to the gut-brain axis.
- Serotonin-Boosting Foods:
- Bananas
- Oats
- Complex Carbohydrates for Steady Blood Sugar:
- Sweet potatoes
- Legumes (beans, lentils)
- High-Fiber Foods for Gut Health:
- Vegetables (carrots, beets)
- Whole grains (barley, oats)

Implementing a Plant-Based Diet
A plant-based diet can enhance your health by incorporating more fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, and seeds into your meals. This shift can help improve digestion, reduce bodily inflammation, and heighten energy levels.
Transition Strategies
- Start Slowly: Integrate plant-based meals into your diet gradually. Begin with one plant-based meal daily, and slowly increase as you feel comfortable.
- Find Replacements: Identify plant-based substitutes for animal products you commonly consume. For example, use almond milk instead of cow’s milk or lentil pasta instead of traditional pasta.
- Educate Yourself: Learn about the nutritional value of various plants to ensure you get all the essential nutrients. A balanced plant-based diet should include a variety of foods to provide a full range of vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how your body responds as you introduce more plant-based foods. Adjust your diet as needed to ensure you’re feeling energized and satiated.
Meal Planning and Preparation
- Creating a Weekly Menu: Plan your meals for the week, including a diverse selection of plants.
- Prep in Advance: To save time, prepare components of your meals ahead of time. Cook a batch of grains, chop vegetables, or make a plant-based sauce during the weekend for easy assembly during the week.
- Seasoning is Key: Use herbs, spices, and seasonings to add flavor to your dishes without the need for animal products. Experiment with different combinations to discover what you enjoy most. Trying new foods is the fun part!
Love Yourself Holistic invites you to further explore the health benefits of plant-based nutrition. Transitioning to a new eating style doesn’t have to be daunting—there is no need to overhaul your diet in one go. It is important to be informed and learn the benefits of the foods we eat.
Take your time to make mindful choices about your meals, focusing on foods that rejuvenate and restore your body. Get creative in the kitchen by trying various recipes and savoring new flavors. Embrace the abundance that a plant-based diet offers. Each meal is an opportunity to promote healing and keep inflammation at bay. It is ok to make the changes one step at a time. Enjoy the journey!